Welcome to our website darasahuru.co.tz, in this article, Are you looking for Physics Form One Topic 8: Work, Energy And Power - Physics Notes Form One Free Download
WORK
Is the product between force applied and the distance in the same direction
Mathematically:

The SI unit of work is Joule (J)
Joule is a force of 1N that moves an object through a distance of 1m in the same direction of the force
Equivalent Units of Work are: 1Nm = 1Joule = Kgm2S-2 = 0.001 KJ
Examples of work done in daily life
When a person pushes a wall (No work is done since d = 0 m)
When a farmer carrying a hole (No work done since d = 0 m)
Lifting a pen (Work is done since d > 0 m)
Lifting a cup (Work is done since d > 0 m)
Example
1. A sack of maize which weights 800N is lifted to height of 2 m. What work done against gravity
Solution:
From:
Wight, w = 800 N Distance, d = 2 m Work done, W.d =?
W.d = F x d
W.d = 800 x 2 = 1600 J
Exercise
1. How much work is done to lift a 7 kg object a distance of 2 m and then hold it at that height for 10 s (ANS: work done to lift = 140 J, Work done to hold = 0 J)
2. A force of 80N pulls a box along a smooth and level ground a distance of 5m. Calculate the work done by force. (ANS: work done = 400J)
3. How much work is done by a force of 10 N in moving an object through a distance of 4 m in the direction of the force. (ANS: Work done = 40 J)
4. Calculate the work done in lifting 200 kg of water through a vertical height of 6 m
(ANS: Work done = 1200 J)
Energy
Energy is the ability of doing work.
The SI unit of energy is Joule (J).
Forms of Energy
Energy can exist in various forms such as:
1. Chemical energy
2. Heat energy
3. Electromagnetic energy
4. Sound energy
5. Electrical energy
6. Nuclear energy
7. Mechanical energy
1. Chemical Energy
Is the energy stored in the food and other fuels. Human get energy from the food that they eat
OR is the energy that results from chemical reactions between atoms or molecules
Example of chemical energy is an electrochemical cell or battery
2. Thermal (Heat Energy)
Is the energy that reflects the temperature difference between two system
Example, A cup of hot coffee has thermal energy.
3. Electromagnetic Energy (Radiant energy)
Is the energy from light or electromagnetic waves
Examples are Infrared radiation, Light energy, Ultraviolet radiation, radio waves, x-rays, Solar energy etc
4. Sound Energy (Sonic Energy)
Is the energy that transfers in the form of waves.
Examples, your voice, Microphone converts sound energy to electrical energy. Loud speaker convert electrical energy to sound energy
5. Electrical Energy
It is due to the kinetic energy of the moving electric charge in a current
6. Nuclear Energy
Is the energy resulting from changes in the atomic nuclei or atomic reactions OR Nuclear energy is the energy from the weak and strong nuclear force.
Examples are nuclear fission, nuclear fusion and Radioactive decay
7. Mechanical energy
Is the energy that results from movement or location of an object
Mechanical energy exists as kinetic and potential energy
Examples, A book sitting on the table (PE), A Moving car (KE) etc
Types of Energy (Mechanical energy)
- Kinetic energy
- Potential energy
Kinetic Energy
Is the energy possessed by a body due to its motion. Examples of kinetic energy are wind energy, Moving water, Ocean Waves
, Ocean Tides, Moving Machines, Falling bodies
Mathematically:

Example
1. An object has a mass of 5kg. What is its kinetic energy if its speed is
(a) 5m/s (b) 10m/s
Data given
Mass, m = 5kg Speed, va = 5m/s Speed, vb = 10m/s
Solution

Individual Assignment
1. What is the kinetic energy of a 12g bullet travelling at 320m/s? (K.E = 6144J)
2. Anna has a mass of 80kg. If she runs at a speed of 10m/s. calculate her kinetic energy (ANS: K.E = 4000J)
POTENTIAL ENERGY
Is the energy possessed by a body due to its state or position.
The potential energy is given by;
Potential Energy = mass x height x acc. due to gravity
The PE can be observed into the following areas;
A boy sitting on a bench
A pen put on the table
A man sleeping on a bed
A book placed onto a table
A ruler put on the table
A man standing on a bus stop
A brick put on the ground etc.
Example
1. A stone of 2kg falls from a height of 25 m above the ground. Calculate potential energy possessed by the stone
Solution:
Mass, m = 2kg Height, h = 25 m
Gravitational force, g = 10N/kg
Transformation of Energy
Energy can be changed from one form to another by the device known as transducer
Transducer
Is a device used to convert energy from one form to another form
For Example,
Battery converts chemical energy to electrical energy
Generator convert mechanical energy to electrical energy
A motor converts electrical energy to mechanical energy
A microphone converts sound energy to electrical energy
Solar panel convert solar energy to electrical energy
Heater converts electrical energy to heat energy
A fan converts electrical energy into mechanical energy
The green plants convert light energy into chemical energy by the process of photosynthesis
Thermal power stations convert heat energy to electrical energy
A torch converts chemical energy to light and heat energy
A bulb converts electrical energy to light and heat energy
Heat engines convert heat energy to mechanical energy
A blender converts electrical energy into mechanical energy
A natural gas stove converts chemical energy from burning into thermal energy
The law of conversation of energy
States that: "Energy can neither be created nor destroyed but can be transferred from one form to another"

Consider the diagram below
At point A and C
The body is momentarily stationary (zero kinetic energy) and has maximum potential energy as it starts swinging to position B (At maximum height, P.Emax = mgh) Since: energy cannot be destroyed (ET = K.E + P.E= 0 + mgh = mgh)
At point B
The bob has maximum kinetic energy which takes it to position C.

2
mv2
NB: At any point the total energy (mechanical energy) is equal to the sum of kinetic energy and potential energy i.e ET = P.E + K.E
Example
1. A stone of mass 2 kg is released from a height of 2m above the ground. Find
a) Total energy
b) Potential energy at heat of 0.5m
c) Kinetic energy at height of 0.5m
d) Velocity acquired at 0.5m
Diagram:

a) Total energy, E =?
Maximum height, h = 2 m Mass of object, m = 2 kg Gravitation force, g = 10 N/kg Minimum velocity, v = 0 m/s From: E = P.E + K.E
E = mgh + 𝟎 = 2 x 10 x2 = 40 J
b) Potential energy, P.E =? Height, h = 0.5m
From: P.E = mgh
P.E = mgh = = 2 x 10 x 0.5 = 10 J
c) Kinetic energy, K.E= ?
From: E = P.E + K.E make K.E, the subject
K.E = E – P.E = 40 – 10 = 30 J
d) Velocity acquired at 0.5m
Velocity acquired at 0.5m, v =?

When the ball rebounds, it rebounds to the height less than the original height. This is due to:-
a) Some energy is used to overcome air resistance as the ball falls
b) The collision between the ball and the ground is not perfectly elastic
c) As the ball hits the ground, some energy is converted into other forms of energy causing its energy to be reduced
Power
Power is the rate of doing work
OR
Power is the rate at which energy is consumed.
Its SI unit is Watt (W)
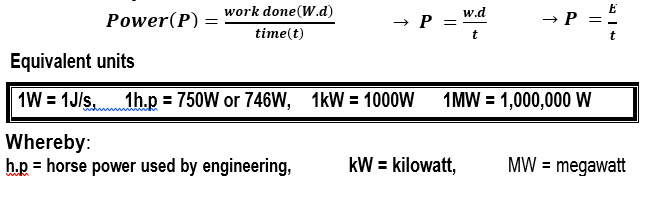
Whereby:
h.p = horse power used by engineering, kW = kilowatt, MW = megawatt
Example
1. A pump raises 100kg of water through a height of 30m in 10s. What is the power developed by the pump
Solution
Given: Mass, m = 100kg Height, h = 30m Time taken, t = 10s
Gravitation force, g = 10N/kg Power, p =?

Assignment
Where necessary use acceleration due to gravity, g =10 m/s2
1 horsepower hp = 746 Watts
1. Define the term work and give its SI unit
2. What happen when force and distance are in the same directions?
3. (a) Define the term power and states how it is measured
(b) Express 6900 J/s in Horsepower
4. A man exerts a force of 200 N for 6 minutes pushing his car 60 m along a horizontal road to reach a garage
a) Calculate the work done by the man. (ANS: E = 12 000 J)
b) Calculate the power of the man when he was pushing the car (P = 33 W)
5. Calculate the power of a pump which can lift 200 kg of water through a vertical height of 6 m in 10 s (Assume g = 10 m/s2) (ANS: P = 1.20 kW)
6. A boy whose mass is 40 kg finds that he can run up a flight of 45 steps, each 16 cm high, in 5.2 s. (Assume g = 10 m/s2) (ANS: P = 0.55 kW)
7. A steady force of 30 N is used to move a small crate across a factory floor. The energy used in moving the crate is 450 J. Calculate the distance moved by the crate (ANS: d = 15 m)
8. Define potential energy and kinetic energy and then state the principle of conservation of energy
9. State four of the transfers of energy which occur at a power station which uses coal as its fuel
10. Define the term energy. A ball of mass 0.2 kg is dropped from a height of 20 m. On impact with the ground, it losses 30 J of energy. Calculate the height it reaches on the rebound. (ANS: h = 5 m)
11. A force of 40 N is applied on a body. The body moves a horizontal distance of 7 m. Calculate the work done on the body. (ANS: Wd = 280 J)
12. A bowling ball is lifted to a height such that its gravitational potential energy is 20 J relative to the ground. If released from rest, how much kinetic energy does the ball have just before striking the ground? Ignore air resistance (ANS: K.E = 20 J)
13. A man whose mass is 75 kg walked up 12 steps of 20 cm each in 5 seconds. Find the power that was developed. (ANS: P = 360 W)
14. A gust of wind shakes loose a football that was stuck in a tree. Ignoring air resistance, if the football falls from a height of 10.8 m, what is its speed just before hitting the ground? (ANS: v = 14.5 m/s)
15. A ball of mass 0.5 kg is dropped from a height of 10 m and on impact with the ground it loses 30 J of energy. Calculate the height it reaches on the rebound (ANS: h = 4 m)
16. Explain why in trying to move a rigid wall, a person is said to be doing no work
17. Define the term work and state its SI unit.
18. A crane is used to lift a body of mass 30 kg through a vertical distance of 6.0 m
a) How much work is done on the body? (ANS: Wd = 1 800 J)
b) What is the P.E stored in the body? (ANS: Wd = 1 800 J)
c) Comment on the two answers (ANS: Wd against the gravity is stored as PE in the body)
19. Name one device which converts:
a) Heat energy into electrical energy
b) Mechanical energy into heat energy
c) Electrical energy into heat energy
d) Electrical energy into sound energy
20. A car of mass 2000 kg is travelling along a straight road at a constant velocity of 10 m/s developing 3.0 kilowatts. If the engine of the car is switched off
i) Calculate the energy lost by the car in coming to rest (ANS K.E =105 J)
ii) Briefly the energy changes in the process stated in (i) above
21. How kinetic energy distinguished from potential energy?
22. If a red ball is higher than a blue ball and both balls have the same mass, which ball has more potential energy?
23. What is the gravitational potential energy of a 3kg ball that is 1 meter above the floor? (ANS: P.E = 30 J)
24. If a 2 kg rock has 200 J of gravitational potential energy, how high is it? (h = 10 m)
25. What is the gravitational potential energy of a 1 kg ball that is 2 meters above the floor? (ANS: P.E = 20 J)
26. A stone of mass 500 g is thrown vertically upwards with a velocity of 15 m/s. find
a) The potential energy at greatest height (ANS: PEE = 56.25 J)
b) The kinetic energy on reaching the ground (ANS: KEE = 56.25 J)
27. Define momentum and Kinetic energy. A car is moving at 36 km/h. Express this velocity in m/s. What velocity will: (ANS: 36 m/s = 10 m/s)
a) Double its momentum (ANS: v = 20 m/s)
b) Double its kinetic energy? (ANS: v = 14 m/s)
28. A motor car of mass 1000 kg travelling at 90 km per hour is brought to rest by the brakes in 100 m. Calculate
a) The car's initial momentum (ANS: p = 25 000 kgm/s)
b) Its initial kinetic energy (ANS: KE = 313 KJ)
c) The average braking force required (ANS: F = 3130 N)
29. The electric motor of a crane uses 42 000 J of electric energy lifting a pack of eight 25 kg bags of cement through a distance of 15 m from the ground to the fourth floor of a block of flats. Calculate the efficiency of the motor during the lifting process (ANS: efficiency = 71 %)
a) The acceleration (ANS: a = 2.5 m/s2)
b) The velocity after 4 s (ANS: v = 10 m/s)
c) The distance moved in 4 s (ANS: d = 20 m)
d) The work done by the force (ANS: Wd = 400 J)

