Welcome to our website darasahuru.co.tz, In this article you will find Physics Form One Topic 9: Light - Physics Notes Form One Free Download
Light is an invisible form of energy that causes the sensation of vision in us through eyes
Sources of Light
Sources of light is the original of light in which the light are comes from whether natural or artificial
Types of Sources of Light
Natural sources of light. For example, sun, star and lighting
Artificial sources of light. For example, torch, candle, kerosene lamp etc
Properties of Light
Light radiates (spread out) from its source
Light travels in straight line
Light transfers energy.
Light travels in vacuum
Light travels at the fast speed, about 300,000,000m/s (300,000 km/s)
NB:
All objects which give out their own light are called Luminous Objects. e.g. star, sun, torch, candle, electric bulb etc
All objects that do not emit their own light instead became visible when they reflect light from another source are called Non-Luminous Objects. E.g. moon
All objects that emit light as a result of being heated are called Incandescent Objects. e.g. light bulb, fire flame, candle flame etc
The spreading of light from its source to the environment in straight lines is referred as Rectilinear Propagation Of Light
Propagation of Light
Light travels in a straight line
Ray
Ray is the path travelled by light .
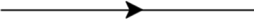
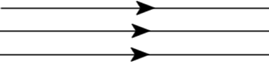
Beam
Beam is a collection of rays of light
Types of Rays
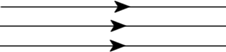
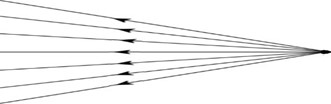
Parallel rays
Converging rays
Diverging rays
Parallel Rays
The collection of rays in a straight line which can never cross each other
Converging Rays
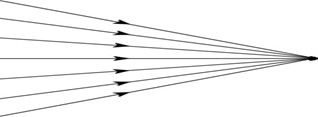
The collection of rays to one point
Diverging Rays
The spreading out of rays from one point
Transmission of Light
Bodies (objects) can be grouped according to transmission of light through them such as:-
a) Opaque bodies
b) Translucent bodies
c) Transparent bodies
Opaque bodies
Are the bodies which do not allow light to pass through them.
For example, stone, wood, concrete walls, books etc
Translucent Objects
Are the objects which allow small amount of light to pass through them.
For example, oiled paper, tinted glass, some plastic materials etc
Transparent Objects
Are the bodies which allow all light to pass through them.
For example, glass, pure water, air etc
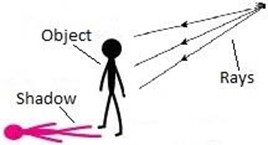
Shadow
Is a dark area where light from a light source is blocked by an opaque object
Types of shadow
Umbra shadow
Penumbra shadow
Umbra Shadow
Is the total shadow formed behind the opaque bodies.
It receives no light at all from the source.
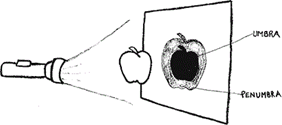
Penumbra Shadow
Is the partial shadow formed behind the opaque bodies.
It receives some light from the source
NB:
When source of light are small than opaque only umbra are formed
Eclipse
Is the shadowing or shading of one heavenly body in the shadow of another.
Types of Eclipse
Solar eclipse
Lunar eclipse
Solar Eclipse
Is the kind of eclipse in which the moon is between the earth and the sun.
Always occurs during the day.
The area covered by the shadow is the umbra in which the sun cannot be seen at all

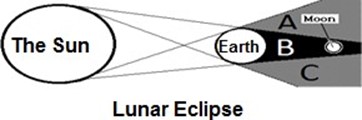
Lunar Eclipse
Is the kind of eclipse in which the earth is between the sun and the moon and the shadow of the earth is cast on the moon.
Reflection of Light
Is the bouncing back of light rays when they meet an obstacle in their path
Terms used
Incident ray is the ray of light which strikes a surface
Reflected ray is the ray that represents the light reflected by the surface

Types of Reflection
i. Regular reflection
ii. Diffuse reflection
i. Regular Reflection
Is the reflection where by all reflected rays reflected in one direction.

The rays are in parallel to each other. Occurs at smooth surface
ii. Diffuse (Irregular) Reflection
Is the reflection where by all reflected rays reflected random or in different directions.

It Occurs at a rough surface
NB:
We can see our images clear in a plane mirror as a result of regular reflection.
If light falls in polished surface at right angle, it is reflected back into the air on the same pass
Diffuse reflection also called scattering/ irregular reflection
When the sun rays enter the earth's atmosphere, it begins to be scattered by molecules of nitrogen and oxygen.
The sky looks blue on a clear sunny day because these molecules scatter the blue light more than other colors due to its shorter wavelength
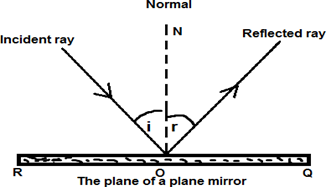
Consider the figure below
From the figure above
ON is a perpendicular line to the surface of the mirror (It is called the Normal)
Normal is the line which divides the angle of incidence and angle of reflection into two equal angles
Angle of incidence (i) is the angle between the incident ray and the normal
Angle of reflection (r) is the angle between the reflected ray and the normal
Thus the laws of reflection states that
1st. "The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal all lie in the same plane"
2nd "The angle of incidence equals to the angle of reflection" ( i = r )
Images Formed by Plane Mirrors
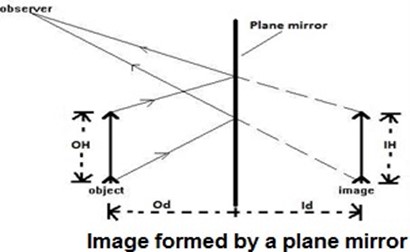
Whereby:
M = magnification Id = image distance
Od = object distance IH = image height OH = object height
Characteristics of Image formed in a Plane Mirror
1. The image is virtual (not real)
2. The image is upright
3. The Image and object have the same size
4. The image distance is the same as the object distance from the plane mirror
5. The image has a left-right reversal (laterally inverted)
Rotating a mirror
The reflected ray moves through an angle twice the angle of rotation
If the mirror was rotated through certain angle θ, then the reflected ray would be rotated through an angle of 2θ
Multiple Mirrors
Is the system which consists of two or more mirrors and produce several images of the same object.
Right – angle mirrors refer to two mirrors that are joined at their edges at an angle of 900
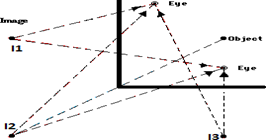
Image in parallel mirrors (two mirrors joined at 00). The image formed is at infinite in each mirror because there is a repetition of images
NB:
The number of images increase as if the angle between the mirrors decreases
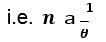
Parallel mirrors are commonly used in saloons and barber shops
The number of images (𝑛) formed between mirrors placed at 𝜽0, is given by the formula:
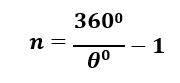
Assignment
1. Define the following terms (with examples)
a) Natural sources of light.
b) Artificial sources of light
2. What is reflection? Distinguish between the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection
3. State the laws of reflection
4. List characteristics of an image formed on a plane mirror
5. Images formed by plane mirrors are laterally inverted. What does this mean?
6. Outline some of the uses of plane mirrors
7. State the difference between umbra and penumbra
8. Differentiate between a ray of light and a beam of light
9. With the help of sketches, show the difference between parallel, diverging and converging beam
10. Define with examples the terms opaque, transparent and translucent as used in light
11. What factors do shadows formed on a screen when opaque object blocks out light depend on?
12. Discuss the application of a periscope 14.How lunar eclipse differ from soar eclipse

14. Explain the formation of multiple images in mirrors inclined at 900
15. The diagram below shows a ray of light reflecting off a mirror. Which is the angle of incidence? Which is the angle of reflection?
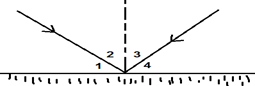
16. Distinguish between regular and diffuse reflection
17. Ahouse building contractor fitted window glass panes which someone cannot see through, but the rooms are fully illuminated with light. These types of glass pane materials are said to be:
A. Dim
B. Opaque
C. Translucent
D. Transparent
21.Give two examples which illustrate that light travels in a straight line
18. The formation of a shadow is evidence that light travels in-------------------
19. Draw a diagram showing a plane reflecting surface, incident ray, reflected ray, the normal, angle of incidence and angle of reflection. What is the relationship between angle of incidence and angle of reflection
20. Describe With the aid of labeled diagrams, the formation of umbra and penumbra shadows. How are they distinguished?
21. Two mirrors are inclined at an angle of 400 to each other. How many images are seen when an object is placed at the center?
22. Differentiate between Opaque and transparent bodies
24. Differentiate between translucent and transparent objects
25. Explain how solar eclipse occur

