Welcome to our website darasahuru.co.tz, are you looking for English form one full notes, Download form one English Notes, English language notes PDF Download, Download notes on Expressing Future Plans And Activities | Topic 10: Expressing Future Plans And Activities, English Form 1, Topic Ten: Expressing Future Plans And Activities - English Form One Notes
Future exists in different forms
(1) Intention - necessity -shall
(2) Probability - possibility -will
Common adverb
Tomorrow, next
How to form future?
Subject + shall/will + be + main clause
Examples:
It will be there tomorrow
Subject + will + be + clause
When we want to talk about things what we shall do tomorrow, next week, next month we use words like
- Going to
- Shall
- Will
Examples:
Tomorrow I’m going to write my mother a letter.
She will tell you something good tomorrow
We shall visit you next month
Going to, will and shall show future tense.
Future continues activities
Subject + will or shall + (be) + verb ........ing + clause
Examples
You will be leaving the school at 4:30pm
We shall be singing in the church choir
Be going to + verb
Use this to talk about activities you planned before.
Remember to change “be” to the correct form for the subject:
I am going to play tennis tomorrow.
You are going to see your cousin next week.
He / She is going to get married in September.
We are going to have a party this weekend.
They are going to save up for a new car.
Question form
As with all verbs that use the verb “to be”, change the subject and the form of the verb to make questions:
Am I going to…?
Are you going to…?
Is he / she going to…?
Are we going to…?
Are they going to…?
Short replies
Yes I am / No I’m not
Yes you are / No you aren’t (or No you’re not)
Yes he is / No he isn’t
Yes we are / No we aren’t (or No we’re not)
Yes they are / No they aren’t (or No they’re not)
Negative form
I am not going to leave my job.
You aren’t going to visit your cousin this week.
He / She isn’t going to get married.
We aren’t going to move house.
They aren’t going to study at university.
Present Continuous
We use the Present Continuous to talk about planned appointments and activities. These are the types of activities that you write in your diary, for example. We often give a time reference.
Very often, “be going to” and the Present Continuous can be used in the same situations.
I’m visiting our new office in London this afternoon. (I’m gong to visit our new office…)
You’re meeting the boss tomorrow. (You’re going to meet the boss…)
He / She is working from home next week. (He is going to work from home…)
We’re taking the train to Scotland. (We are going to take the train…)
They’re leaving later today. (They are going to leave…)
Be planning to / Be thinking of
You can use the verbs “plan” and “think” in the present continuous is to talk about activities that aren’t 100% definite.
I’m planning to study abroad next year.
We’re thinking of getting a dog.
Remember: “be planning to” is followed by the verb; “be thinking of” is followed by a gerund (ing form).
Review of “will”
We can use “will” to talk about the future and make predictions.
For example:
“We won’t have enough money to buy a new house this year.”
“I think he’ll get a promotion next month.”
We can also use “will” to talk about decisions that we make at the time of speaking (NOT decisions that we plan before):
“I’ll help you with your bags.” (at the moment you see someone with a heavy bag)
It is wrong to say “I’m going to help you with your bags” or “I’m helping you with your bags” in this situation.
For more information, see our page on using will.
Future Plans
Exercise
Choose the correct answer.
FUTURE TENSE
The future tense is used when talking about something that will happen in the future. The future is formed by using models; will, shall, and 'be going to'.
The future tense is formed with will or shall and the verb's base form to express an action or state of being that will occur.
FORMS/CATEGORIES OF FUTURE TENSE
There are four forms of Future Tense.
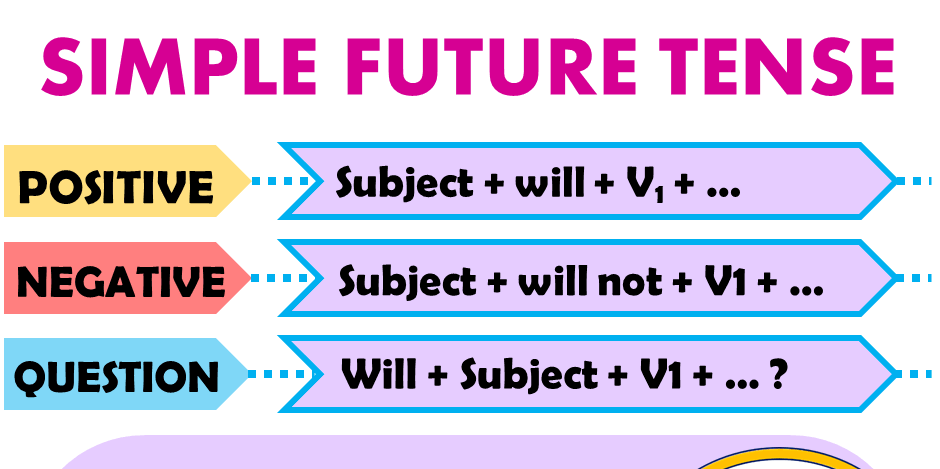
SIMPLE FUTURE TENSE
Positive sentences. Structure Pattern:
S + will/shall + base form of verb
I will wash my clothes
She will cook ugali
They will play football
Contracted forms: Subject + 'ill
I'll wash my clothes
She'll cook ugali
They'll play football
Negative sentences. Structural pattern:
S + will + not + base form of verb.
I will not wash my clothes
She will not cook ugali
They will not play football
Contracted forms 1:
subject + will/shall
I'll not wash my clothes.
She'll not cook ugali.
They'll play football tomorrow.
Contracted Forms 2:
Auxiliary will+ not
I won't wash my clothes
She won't cook ugali
They won't play football
Interrogative Sentences: Structural pattern:
Will/Shall + Subject + base form of verb
Positive Interrogative Sentences. Structural pattern:
Will/Shall + Subject + base form of verb
Will I wash my clothes?
Will Asha cook ugali?
Will they play football?
Negative Interrogative Sentences. Structural pattern:
Won't+ Subject + base form of verb
Won't I wash my clothes?
Won't Asha cook ugali?
Won't they play football?
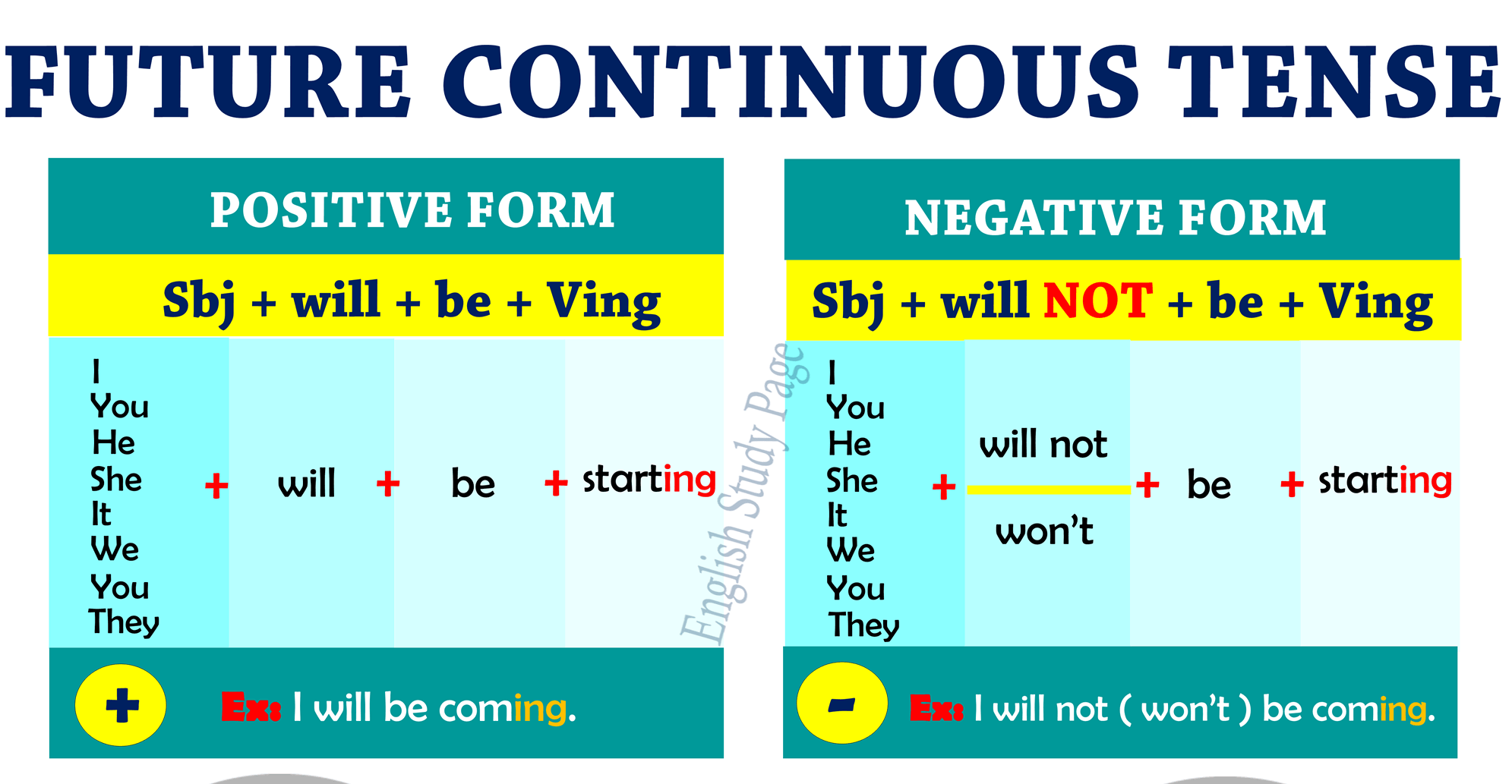
FUTURE CONTINUOUS TENSE
Positive Sentences.
Structural pattern:
Subject + will/shall + be + present participle
I will be washing my clothes
She will be cooking cook ugali
They will playing football
Negative Sentences:
Structural pattern:
Subject + will/shall + be + present participle.
I will not be washing my clothes
She will not be cooking cook ugali
They will not be playing football
Interrogative Sentences. Structural pattern:
Will/shall + subject + be + -ing.
Positive Interrogative Sentences. Structural pattern:
Will/shall + subject + be + -ing.
Will I be washing my clothes?
Will she be cooking cook ugali?
Will they be playing football?
Negative Interrogative Sentences. Structural pattern:
Won't+ subject + be + -ing.
Won't I be washing my clothes?
Won't she be cooking cook ugali?
Won't they be playing football?
FUTURE PERFECT TENSE
Positive Sentences.
Structural pattern:
Subject + will/shall + has/have + past participle
I will have washed my clothes
She will has cooked ugali/She will have cooked ugali
They will have played football
Note:
These are mostly used with prepositions of time. Examples.
By 16.00, I will have finished my homework.
Before evening, they will have arrived.
Negative Sentences.
Structural pattern:
Subject + will/shall + not + has/have + past participle
I will have not washed my clothes
She will has not cooked ugali/She will have cooked ugali
They will have not played football
Interrogative Sentences.
Structural pattern:
Will/shall + subject + has/have + past participle.
Positive Interrogative Sentences.
Structural pattern:
Will/shall + subject + has/have + past participle
Will I have washed my clothes?
Will she has cooked ugali/Will she have cooked ugali?
Will they have played football?
Negative Interrogative Sentences.
Structural pattern:
Won't+ subject + has/have + past participle.
Won't I have washed my clothes?
Won't she has cooked ugali/Will she have cooked ugali?
Won't they have played football?
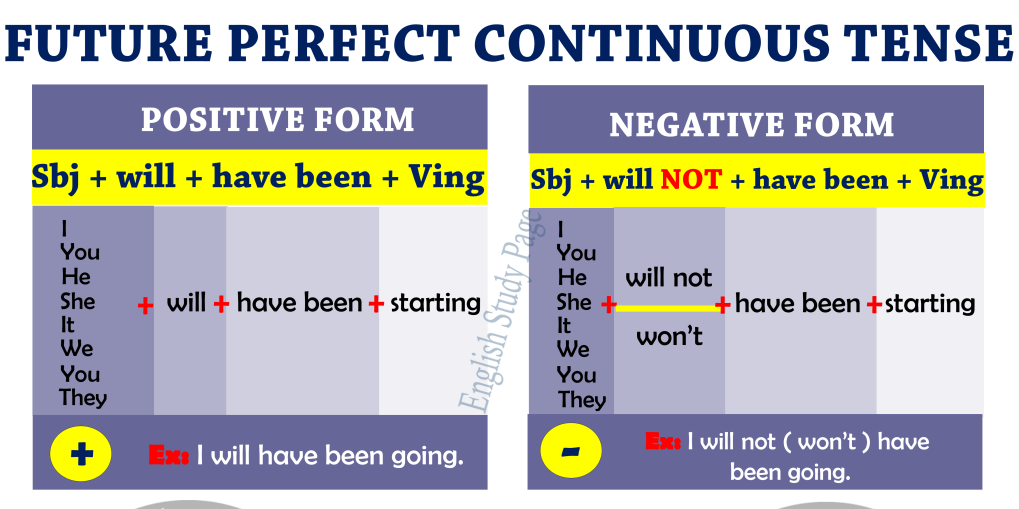
FUTURE PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE
Positive Sentences:
Structural pattern:
Subject + will/shall + has/have + been + present participle
I will have been washing my clothes
She will has been cooking ugali/She will have been cooking ugali
They will have been playing football
Negative Sentences.
Structural pattern:
Subject + will/shall + not + has/have + been+ present participle
I will have not been washing my clothes
She will not has been cooking ugali/She will not have been cooking ugali
They will not have been playing football
Interrogative Sentences.
Structural pattern:
Will/shall/Won't + subject+ has/have + been+ past participle
Positive Interrogative Sentences.
Structural pattern:
Won't+ subject+ has/have +been + past participle.
Will I have been washing my clothes?
Will she has been cooking ugali/Will she have been cooking ugali?
Will they have been playing football?
Negative Interrogative Sentences.
Structural pattern:
Won't + subject + has/have + been + past participle.
Won't I have been washing my clothes?
Won't she has been cooking ugali/Will she have been cooking ugali?
Won't they have been playing football?
OTHER FUTURE TENSE USAGE
Future tense can also be expressed in other various ways:
DECISIONS, INTENTIONS AND ARRANGEMENTS
In making decisions, intentions and arrangements, the sentences in future tense express something which has been decided, intended or arranged.
I'm going home now
The people will be leaving the conference
I'm staying in tonight
We are to be patient
We are to be informed by post
Will you be staying long?
PREDICTIONS
We can also make predictions by using future tense.
That dog is going to cause problem if it's untied.
There won't be light before 6 a.m.
That player is going to be booked.
He will have had the operation by next month.
I will have had taken the vacation.
They will have been travelling for eight months by the end of May.
Teachers will have been taking teaching break by December.
(Future perfect continuous tense expressing predictions)
EXPRESSING FUTURE PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
EXPRESSING FUTURE IN THE PAST
The future action expressed in the past is the action that was about to happen but something obstructed it.
I was going to tell you about it but I failed.
I was about to tell you something when the door was knocked.
They were about to start the game but the weather changed.
The results were due to come out
The cargo was due to have arrived this morning.
OTHER WAYS OF EXPRESSING THE FUTURE
Other ways used to express future plans are introduced by some special words. The mostly used words are: due and about.
The train is due to start the journey.
The President is about to leave.
Road construction is due to start in May.
Hurry! We're about to leave.
We'll leave when the rain has stopped.
Exercise
1. Mention 4 things that you are going to do after you have finished form four
(i) ..........................
(ii) ..........................
(iii) ..........................
(iv) ..........................
(v) ..........................
2. Mention three (3) things which will happen to someone who has HIV/AIDS
(i) ..........................
(ii) ..........................
(iii) ..........................
Note:
will is used all persons in the singular and plural for example
1. I will be wait
2. I will go to the market tomorrow
Shall is sometimes use instead of will, It is used in statement in the first personal singular or plural, It shows determination or promise about future activities for example
i) We shall play hard and we shall win the game: (determination)
ii) I shall write to you as soon as i arrive in Mpwapwa (promise)