Welcome to our website darasahuru.co.tz, in this post you will find Topic 8: Pythagoras Theorem - Mathematics Study Notes Form II, Form Two Mathematics Notes, PDF Pythagoras Theorem Free Download, Pythagoras Theorem, Form II Pythagoras Theorem Notes, Mathematics for Form Two Study Notes.
Topic 8: Pythagoras Theorem - Mathematics Study Notes Form II
Pythagoras Theorem
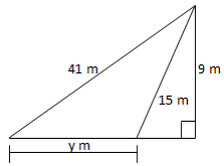
Triangle with a Right angle i.e. 90° has an amazing property. Do you want to know what property is that? Go on, read our notes to see the amazing property of a right angled triangle.
This kind of a Triangle is called Right angled triangle. When triangle is a right angled triangle, squares can be made on each of the three sides. See illustration below:
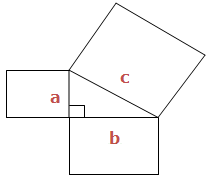
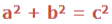
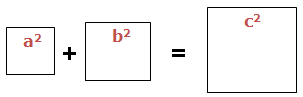
‘c’ is the Longest side of the Triangle, is called Hypogenous and is the one that forms the biggest square. a and b are the two smaller sides.
Proof of Pythagoras Theorem
The Pythagoras Theorem
Prove the pythagoras theorem
See the figure below:
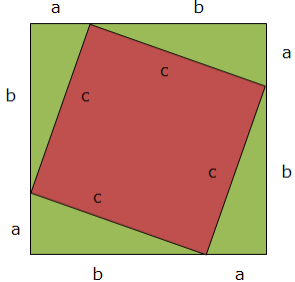
The area of a whole square (big square)
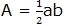
But there are 4 triangles and they are equal, so total area =
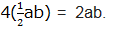
Both areas must be equal, the area of a big square must be equal to the area of a tilted square plus the area of 4 triangles
Exercise 1
- c if a = 5 and b = 12
- a if b = 8 and c = 12
- b if a = 9 and c = 11
2. A rectangle has base 6 and height 10. What is the length of the diagonal?
3. A square has a diagonal with length 6. What is the length of the sides of the square?
The Pythagoras Theorem
Prove the Pythagoras theorem
The area of a whole square (big square)
Second, area of the equal triangles each with bases a and height b:
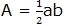
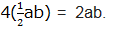
Both areas must be equal, the area of a big square must be equal to the area of a tilted square plus the area of 4 triangles
Exercise 2
- c if a = 5 and b = 12
- a if b = 8 and c = 12
- b if a = 9 and c = 11
3. A square has a diagonal with length 6. What is the length
Application of Pythagoras Theorem
The Pythagoras Theorem to Solve Daily Life Problems
Apply the Pythagoras theorem to solve daily life problems
Activity 1
Apply the Pythagoras theorem to solve daily life problems